Infertility is usually considered the inability to conceive following a year or more of unprotected sexual intercourse. This gap may be shorter if the woman is 35 years or older at the start of attempts to conceive. Problems with conception may derive from egg release, fertilization by the sperm, zygote transport through the tube to the uterus, or implantation in the uterine lining.
Many cultures attribute infertility solely to the female partner. However, it is abundantly clear that the causes of infertility may be traceable to male or female factors, or both, or even none.
Hormonal causes due to genetic or environmental factors also operate in female infertility, as may be seen in polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), functional amenorrhea, or disorders of the hypothalamo-pituitary axis. Diminished ovarian reserve or premature ovarian insufficiency may also cause difficulty in conception.
Physical obstruction of the tubes or uterine cavity, or chemical interference with their productive milieu, can also cause female infertility as a sequel of pelvic infection, endometriosis, earlier pelvic or abdominal surgery, or sexually transmitted infections
In men, who may contribute to infertility in a significant proportion of cases, semen analysis could show disorders of sperm number, motility or morphology.
Conditions like varicoceles (dilated tortuous testicular veins), testicular trauma, alcoholism, smoking, drug abuse and some types of medical or surgical treatment may all lead to diminished male fertility.
Apart from physical causes, interference with the hypothalamo-pituitary hormonal function may disrupt testicular sperm production. Anabolic steroid use may fall into this category.
Certain genetic factors may also lead to abnormalities of the Y chromosome that is key to sperm production. Finally, excessively high temperatures maintained over a prolonged period in the testes may lead to male infertility, as could environmental toxins such as pesticides and heavy metals.
GET TREATED SOONER, NOT LATER
Infertility may sometimes be relieved on its own, but the chances are typically not reassuring. Some couples believe that adoption betters the chances of conceiving in the future, but this is not to be relied upon, according to most experts.
Couples who want to have their own children should consult their physician without delaying too long, keeping in view the diminishing chances of fertility and of a successful pregnancy, as well as the increased risk of medical illness, with increasing age in either partner.
What about IVF?
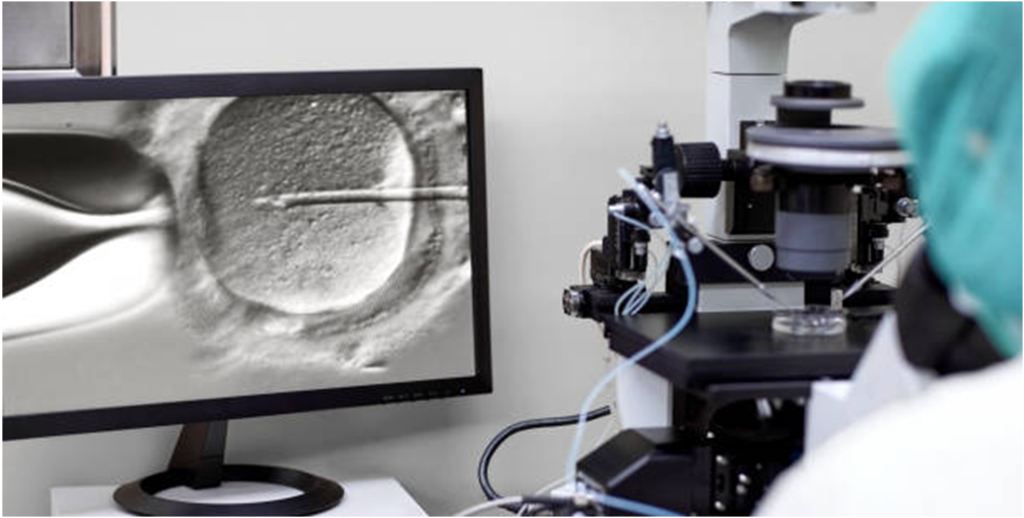
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is among the most commonly used techniques of assisted reproduction. In this method, ova are retrieved from the woman’s body following the induction of super ovulation. That is, the woman is put on a medical regimen that allows multiple eggs to mature during a single cycle, as compared to the one that typically matures during a normal ovarian cycle.
The eggs are retrieved, and combined with the sperm from the partner, or if otherwise determined by the couple, from another man. This leads to fertilization and the formation of an embryo. After3-5days, the embryo is transferred into the woman’s uterus, or else frozen for future cycles–the
frozen embryo transfer.
IVF has been around for over four decades, and millions of babies have been born using this technology. The greatest ethical issue with IVF relates to the fate of the extra embryos, which are most often used for research if the parents do not want to, or cannot afford to, use them to try having more children. For many, this amounts to aborting one’s own children.
IVF benefits multiple causes of infertility
IVF is used to overcome infertility due to egg deficiency, as in older women, for instance. It can also help counter chromosomal anomalies by selecting normal eggs for fertilization. Moreover, tubal factors associated with infertility can be treated by IVF which by passes the tubal transport factor.
This is also the case with PCOS, where the endocrine milieu suppresses normal ovulation. A very low sperm count in men can also be overcome using IVF, as also if the sperm are immotile. Finally, recurrent miscarriage or failure of fertility treatment can also indicate the utility of IVF.
Many people think that IVF is used only for the treatment of infertility. However, in today’s much-changed moral environment, parents often elect to have only ostensibly genetically normal offspring. In order to achieve this, they may choose to have IVF where previously screened gametes are used for fertilization.
PRE-IMPLANTATION GENETIC TESTING
PGT is one procedure used to detect the presence of a genetic disorder or a chromosomal abnormality in an embryo created using IVF. After allowing the embryo to cleave sufficiently, one or more cells are removed for genetic testing so that only normal embryos are used, going forward.
Less effective with age some couples assume that IVF can surmount the natural waning of a female’s reproductive capabilities. However, this is not quite true, because the female body may not be able to generate mature highly-functioning ova capable of forming a healthy embryo, beyond a certain point. Moreover, even if fertilization occurs, the female body may be too old to carry the pregnancy successfully to term.
The truth is that the chances of conception range from 25-50% per month, in a woman’s20s. Female fertility often declines markedly from the mid-30s onwards, and by the age of 40, the chances of conception are as low as5%.
The use of IVF does compensate partly for this age-related drop in fertility, but the chances of alive birth following a complete IVF cycle drops from 43% in the early 30s, through 30% in the second half of the 30s, to just over 10% at the age of 40-44 years.
Men can father children at any age. The age of the male partner also affects the chances of pregnancy, recent research has shown. Male fertility also begins to drop after the age of 40-45 years. This could, therefore, also hamper the conception and live birth rate after.
IVF CAUSES MULTIPLE BIRTHS
Another misconception is that the use of IVF is inevitably linked to multiple births. While this is related to the earlier practice of transferring multiple embryos to enhance the chances that one, at least, would continue to grow, modern practice takes advantage of better technology to transfer two or fewer embryos with a much higher chance of successful pregnancy. Infact, multi-embryo transfer is today associated with a lower live birth rate than single or two-embryo transfer.
IVF IS NOT A PANACEA
Infertility can be due to multiple factors, some of which may interact. As a result, IVF may not be the best or only option for an infertile couple, barring genetic factors. For instance, tubal abnormalities, uterine issues or hormonal imbalances may all play a role that can be corrected without IVF.

Vamtam
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipiscing elit dolor
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS: COST OF IVF IN LAGOS, IVF SUCCESS RATE, SIDE EFFECTS.
July 17, 2023
WHO IS IN VITRO FERTILIZATION (IVF) SUITABLE FOR? Couples who have been diagnosed with a variety of infertility challenges and have not been able to
